Aug 12 • Jordan Felber
Is AutoCAD Still in Demand?
Related — AutoCAD Training for Landscape Designers
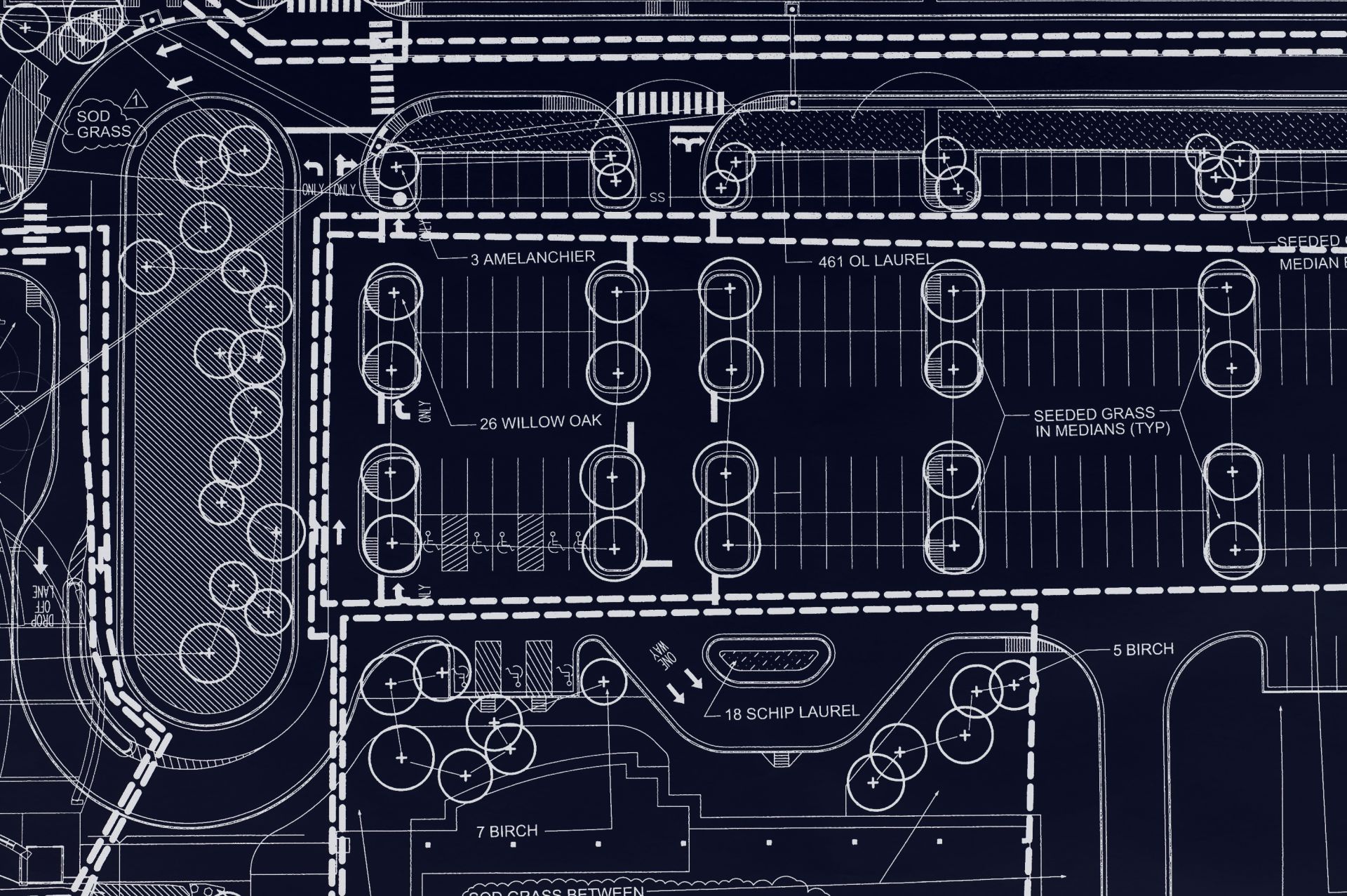
For decades, AutoCAD has been a cornerstone of the design world, enabling architects, engineers, and landscape designers to create precise, professional-grade drawings.
While newer 3D modeling and visualization tools have emerged, many wonder whether AutoCAD still holds its place in today’s evolving design workflows.
In an era where immersive rendering, parametric design, and AI-driven planning are gaining attention, is AutoCAD still worth learning—and using?
In the fields of landscape architecture and the broader AEC (Architecture, Engineering, and Construction) industry, the answer is a strong “yes.”
Not only does AutoCAD remain relevant, but it continues to be an essential foundation for design documentation, collaboration, and project delivery.
While newer 3D modeling and visualization tools have emerged, many wonder whether AutoCAD still holds its place in today’s evolving design workflows.
In an era where immersive rendering, parametric design, and AI-driven planning are gaining attention, is AutoCAD still worth learning—and using?
In the fields of landscape architecture and the broader AEC (Architecture, Engineering, and Construction) industry, the answer is a strong “yes.”
Not only does AutoCAD remain relevant, but it continues to be an essential foundation for design documentation, collaboration, and project delivery.
1. AutoCAD’s Legacy and Longevity in the Design Industry
Since its launch in 1982, AutoCAD has defined how technical drawings are created and shared. Its transition from simple 2D drafting to an advanced platform with 3D capabilities and specialized toolsets has kept it relevant for over four decades.
In the landscape design world, AutoCAD is the industry standard for creating base plans, planting layouts, grading plans, and construction details. Many clients, contractors, and municipal agencies still expect deliverables in DWG format, and AutoCAD’s precision ensures these plans meet strict standards.
The AEC industry reinforces AutoCAD’s staying power. Architectural and engineering firms rely on AutoCAD’s compatibility across disciplines, meaning landscape designers who work with architects and civil engineers benefit from using a platform that seamlessly integrates into broader project workflows. While design software trends come and go, AutoCAD’s ability to adapt to industry needs has made it a lasting fixture.
In the landscape design world, AutoCAD is the industry standard for creating base plans, planting layouts, grading plans, and construction details. Many clients, contractors, and municipal agencies still expect deliverables in DWG format, and AutoCAD’s precision ensures these plans meet strict standards.
The AEC industry reinforces AutoCAD’s staying power. Architectural and engineering firms rely on AutoCAD’s compatibility across disciplines, meaning landscape designers who work with architects and civil engineers benefit from using a platform that seamlessly integrates into broader project workflows. While design software trends come and go, AutoCAD’s ability to adapt to industry needs has made it a lasting fixture.
2. Industries That Still Rely Heavily on AutoCAD for Landscape Design
While technology in the design world continues to evolve, several industries still consider AutoCAD an essential part of their workflow. In landscape design, its precision and compatibility with other disciplines make it the go-to choice for creating and sharing technical drawings.
From architectural site plans to civil engineering layouts, AutoCAD remains the common language that keeps projects moving seamlessly from concept to construction.
AutoCAD remains indispensable in several key areas that directly impact landscape designers:
From architectural site plans to civil engineering layouts, AutoCAD remains the common language that keeps projects moving seamlessly from concept to construction.
AutoCAD remains indispensable in several key areas that directly impact landscape designers:
Architecture & Site Development
Architects and site planners frequently incorporate landscape drawings into their overall project plans. Because AutoCAD is used extensively in architectural firms, landscape designers who draft in AutoCAD can exchange files without formatting issues, preserving accuracy and detail.
Civil Engineering & Infrastructure
From grading plans to stormwater management, civil engineers often require site information in AutoCAD format. Landscape designers working on public parks, urban plazas, or streetscapes can easily collaborate by delivering plans in a universally accepted format.
Landscape Architecture
AutoCAD provides the precision needed to translate conceptual ideas into buildable construction documents. Designers can create scaled planting plans, irrigation layouts, and hardscape details that align perfectly with architectural and engineering drawings.
Construction & Installation
On the construction side, AutoCAD drawings guide contractors with exact measurements, material specifications, and installation sequences. This reduces errors in the field and ensures the design intent is realized.
In each of these sectors, AutoCAD isn’t just “useful”—it’s the language professionals speak to coordinate across disciplines.
In each of these sectors, AutoCAD isn’t just “useful”—it’s the language professionals speak to coordinate across disciplines.
In 4 weeks or less, learn how to use AutoCAD to create 2D landscape designs and plans.
Learn About Online Course Here
Learn About Online Course Here
3. How AutoCAD Compares to Emerging Software
There’s no denying the growing popularity of newer design tools like Rhino, SketchUp, Vectorworks, and Revit. These programs often excel in specific areas—Rhino for complex 3D modeling, SketchUp for quick conceptual work, Revit for BIM coordination—but AutoCAD remains the backbone of detailed documentation.
Compatibility Over Competition
Rather than being replaced by these tools, AutoCAD often works alongside them. For example, a landscape designer might use SketchUp or Rhino to model a 3D concept, then bring that geometry into AutoCAD for precise detailing and documentation. Similarly, AutoCAD drawings can be linked to Revit models for integrated project coordination.
Universality in File Exchange
The DWG file format is one of the most widely supported in the AEC industry. Even if a project’s primary modeling is done in another platform, AutoCAD often serves as the final checkpoint for creating, editing, and sharing construction-ready drawings.
Precision for Construction
While newer tools offer faster modeling workflows, AutoCAD’s strength lies in its exactness. The ability to draft with pinpoint accuracy is critical when producing plans that contractors will follow to the inch.
In 4 weeks or less, learn how to use AutoCAD to create 2D landscape designs and plans.
Learn About Online Course Here
Learn About Online Course Here
4. Career Opportunities and Skills Demand for AutoCAD Users
For landscape designers, AutoCAD proficiency is not just a resume booster—it’s often a job requirement. Many landscape architecture firms list AutoCAD among their top must-have skills for new hires, especially for roles involving technical production.
Why Employers Value AutoCAD Skills
- Collaboration: Most multidisciplinary teams still use AutoCAD for shared drawings.
- Efficiency: Experienced users can draft plans quickly, meeting tight deadlines without sacrificing accuracy.
- Adaptability: AutoCAD skills transfer easily between different sectors of the AEC industry.
A quick search on popular job boards reveals thousands of listings worldwide that call for AutoCAD expertise, from entry-level drafting positions to senior design roles. Even as technology shifts, firms know that AutoCAD-trained professionals can step into projects and work seamlessly with the rest of the team.
For independent landscape designers, AutoCAD also opens the door to larger projects. Being able to deliver professional, industry-standard drawings means working with architects, engineers, and municipalities on projects that require a high level of technical accuracy.
For independent landscape designers, AutoCAD also opens the door to larger projects. Being able to deliver professional, industry-standard drawings means working with architects, engineers, and municipalities on projects that require a high level of technical accuracy.
In 4 weeks or less, learn how to use AutoCAD to create 2D landscape designs and plans.
Learn About Online Course Here
Learn About Online Course Here
5. The Future of AutoCAD: Adaptation and Specialization
Far from stagnating, AutoCAD has evolved to meet the demands of modern design workflows. Autodesk has introduced cloud storage, mobile apps, and subscription-based licensing to make AutoCAD accessible anywhere.
Integration with Other Technologies
AutoCAD continues to improve interoperability with BIM platforms like Revit and environmental analysis tools like Civil 3D. This matters for landscape architects working on complex sites where grading, drainage, and planting must be coordinated with buildings and infrastructure.
The Bottom Line
AutoCAD’s ongoing updates, combined with its entrenched position in the AEC industry, mean it will remain in demand for the foreseeable future. While it’s wise for designers to expand their skillsets with emerging 3D tools, AutoCAD proficiency remains the foundation on which many successful careers—and projects—are built.
In 4 weeks or less, learn how to use AutoCAD to create 2D landscape designs and plans.
Learn About Online Course Here
Learn About Online Course Here
FAQs
Is AutoCAD still in demand?
Yes. AutoCAD remains one of the most widely used design platforms in the AEC industry, especially in landscape architecture. Its universal DWG format, precision drafting capabilities, and compatibility with other design software ensure it continues to be a must-have skill for professionals.
Should I learn AutoCAD or Revit for landscape design?
Both have value, but AutoCAD is often the starting point. It excels at detailed 2D documentation, which is essential for planting plans, hardscape layouts, and construction details. Revit is better suited for BIM coordination on large-scale, multidisciplinary projects. Many landscape designers use AutoCAD as their primary drafting tool and integrate it with Revit when needed.
What jobs require AutoCAD skills in landscape design?
Jobs in landscape architecture firms, multidisciplinary design studios, and urban planning agencies often require AutoCAD proficiency. Roles include landscape designer, CAD technician, design associate, and project coordinator. Contractors and consultants also use AutoCAD to interpret and execute design intent.
Is AutoCAD being replaced by newer software?
No, AutoCAD is not being replaced—it’s being complemented. Tools like Rhino, SketchUp, and Vectorworks may offer faster modeling or visualization features, but AutoCAD remains the standard for technical documentation and project coordination.
How can landscape designers stay competitive using AutoCAD?
By pairing AutoCAD skills with knowledge of 3D modeling, rendering, or GIS integration, designers can offer end-to-end services. Combining AutoCAD’s precision with visualization tools like Rhino or Enscape makes designers more versatile and competitive in the market.
In 4 weeks or less, learn how to use AutoCAD to create 2D landscape designs and plans.
Learn About Online Course Here
Learn About Online Course Here

The Landscape Library Academy is an online platform teaching landscape professionals, students, homeowners and enthusiasts how to design landscapes and master software for the field.
The Landscape Library Academy is the education division of The Landscape Library.
Click here to visit TheLandscapeLibrary.com for media including education articles, projects features and more.
The Landscape Library Academy is the education division of The Landscape Library.
Click here to visit TheLandscapeLibrary.com for media including education articles, projects features and more.
Copyright © 2025